Quickstart: instrument a Ruby service with OBI
You are viewing the English version of this page because it has not yet been fully translated. Interested in helping out? See Contributing.
1. Run an instrumentable Ruby service
Run an instrumentable Ruby service or download and run a simple example Ruby HTTP service.
curl -OL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/grafana/beyla/main/examples/quickstart/ruby/quickstart.rb
ruby quickstart.rb
2. Download OBI
Download the latest OBI executable from the
OBI releases page. Uncompress and
copy the OBI executable to any location in your $PATH.
4. Run OBI with minimal configuration
To run OBI, first set the following environment variables:
- The
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL,OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINTandOTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERSvariables copied from the previous step. OTEL_EBPF_OPEN_PORT: the port the instrumented service is using (for example,80or443). If using the example service in the first section of this guide, set this variable to8080.
To facilitate local testing, set the OTEL_EBPF_TRACE_PRINTER=text environment
variable. When this option is set, OBI prints traces in text format to the
standard output.
OBI automatically reports the name of the process executable as service name:
ruby. To override it, refer to the
override service name and namespace
documentation section.
Notice: OBI requires administrative (sudo) privileges, or at least it needs to
be granted the CAP_SYS_ADMIN capability.
export OTEL_EBPF_OPEN_PORT=8080
export OTEL_EBPF_TRACE_PRINTER=text
export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL="http/protobuf"
export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT="https://otlp-gateway-prod-eu-west-0.grafana.net/otlp"
export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS="Authorization=Basic ...your-encoded-credentials..."
sudo -E beyla
5. Test the service
With OBI and the service running, make HTTP requests to the instrumented service:
curl http://localhost:8080/foo
OBI should output traces to the standard output similar to this:
2024-01-09 10:31:33.19103133 (3.254486ms[3.254486ms]) 200 GET /foo [127.0.0.1]->[127.0.0.1:8080]
size:80B svc=[{quickstart ruby lima-ubuntu-lts-5074}] traceparent=[00-46214bd23716280eef43cf798dbe5522-0000000000000000-01]
The above trace shows:
2024-01-09 10:31:33.19103133: time of the trace(3.254486ms[3.254486ms]): total response time for the request200 GET /foo: response code, HTTP method, and URL path[127.0.0.1]->[127.0.0.1:8080]source and destination host:portsize:80B: size of the HTTP request (sum of the headers and the body)svc=[{quickstart ruby lima-ubuntu-lts-5074}]:quickstartservice, running in Ruby, with an automatically created service instance namelima-ubuntu-lts-5074traceparentas received by the parent request, or a new random one if the parent request didn’t specify it
After a few minutes traces will appear in Grafana Cloud. For example, in the traces explorer:
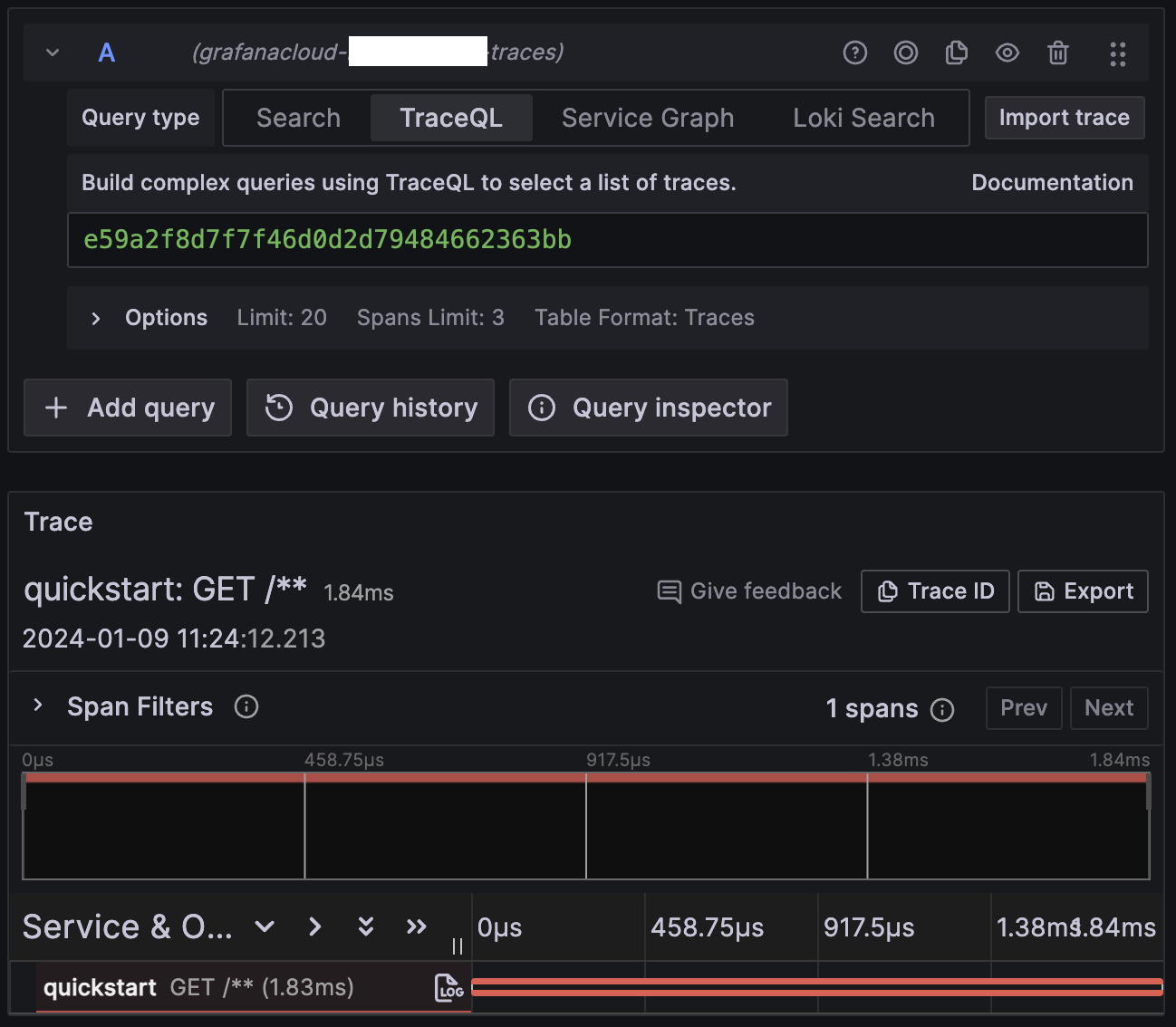
6. Configure routing
The exposed span name in Grafana Cloud is a generic GET /**, where it should
say something like GET /foo (the path of the test request URL).
OBI groups any unknown URL path as /** to avoid unexpected cardinality
explosions.
Configure routing to tell OBI about expected routes.
For this quickstart, let OBI to heuristically group the routes.
First, create a config.yml file with the following content:
routes:
unmatched: heuristic
Then, run OBI with the -config argument (or use the OTEL_EBPF_CONFIG_PATH
environment variable instead):
sudo -E beyla -config config.yml
Finally, make HTTP requests:
curl http://localhost:8080/foo
curl http://localhost:8080/user/1234
curl http://localhost:8080/user/5678
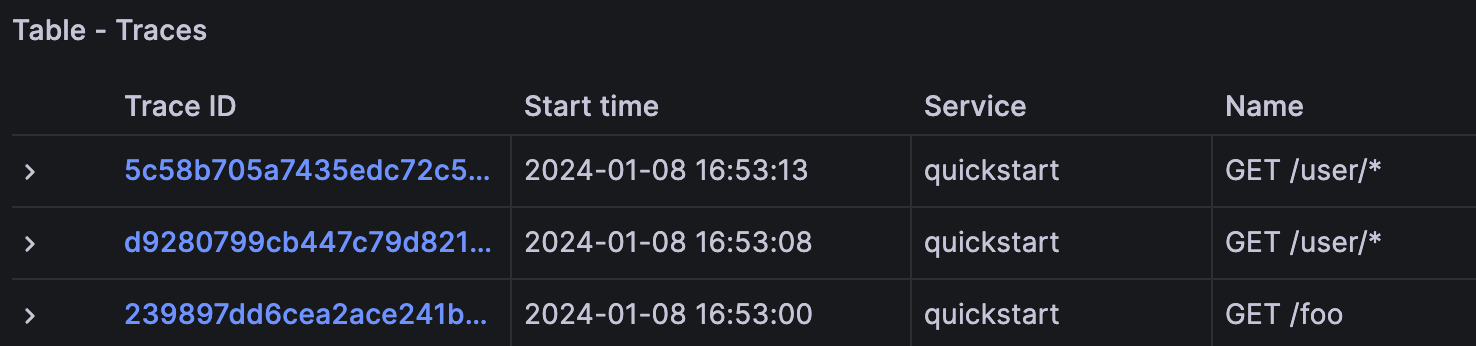
Grafana will now heuristically assign a route to each trace. /foo got its own
route while /user/1234 and /user/5678 were grouped into the /user/* route.
Next steps
- Get more details of the different OBI configuration options.
- Learn how to deploy OBI as a Docker container or as a Kubernetes DaemonSet or sidecar.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Thank you. Your feedback is appreciated!
Please let us know how we can improve this page. Your feedback is appreciated!